Research
A major challenge in human genetics is determining which noncoding sequences act as enhancers or promoters, which genes they regulate and through which mechanisms, and in which cell types these activities are present.
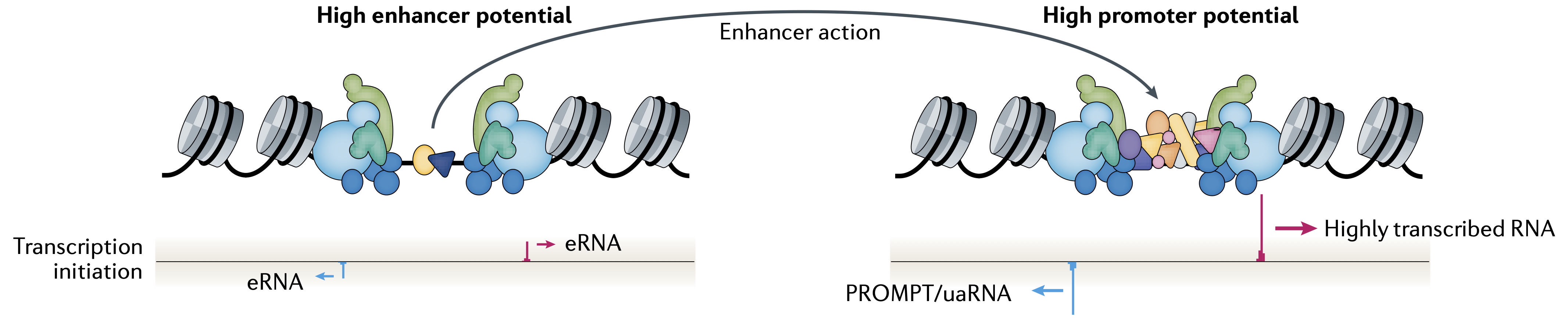
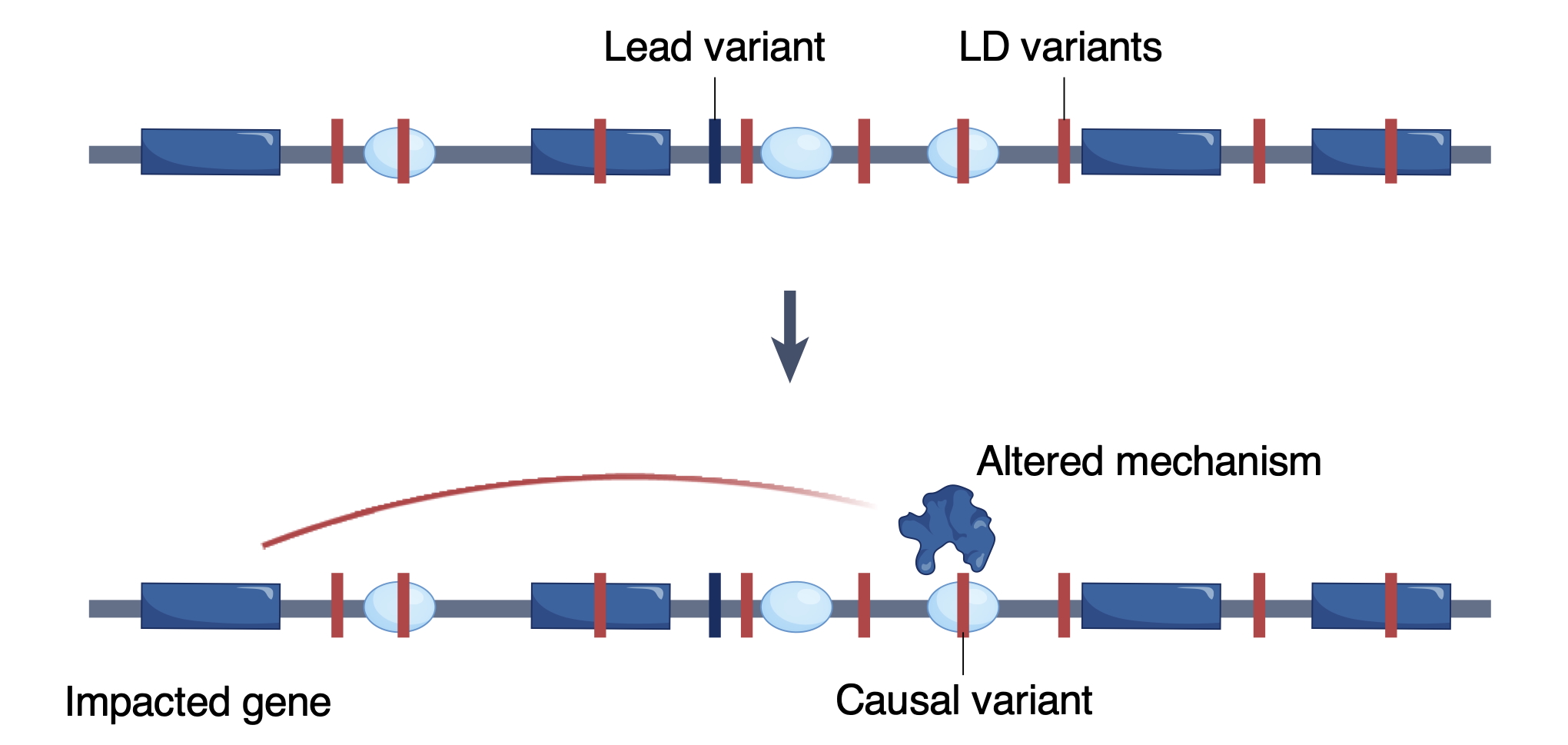
Regulation of gene expression is one of life’s most fundamental biological processes and it influences all aspects of human biology. Consequently, dysfunction of gene regulation has emerged as a central mechanism in the pathogenesis of human diseases. Human genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have discovered hundreds of thousands of associations between genetic variants and human diseases or phenotypic traits. A majority of these associations involve non-coding variants that overlap gene regulatory elements, in particular enhancers and promoters. However, it has proven challenging to connect GWAS associations to their causal mechanisms, because we do not fully understand the logic by which our genome encodes for regulatory activity and cell-type specific functions, and how these activities are mediated by regulatory proteins. Therefore, there is a great need for accurate computational models of gene regulation that can be used to interpret the impact of genetic variants on molecular phenotypes and how these translate to disease risk.
Research aims
To characterize fundamental gene regulatory mechanisms and gain insights into molecular mechanisms by which enhancer or promoter dysregulation contributes to disease risk, we focus on developing computational tools, predictive models, and experimental assays to:
- Determine which genomic sequences act as enhancers or promoters
- Map enhancer-gene regulatory interactions
- Determine the cell types in which these activities are present
- Learn how the human genome encodes regulatory activity
- Determine the function of regulatory genetic variants
Representative work
- Andersson R, et al. An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature. 2014
- Rennie S, et al. Transcription start site analysis reveals widespread divergent transcription in D. melanogaster and core promoter-encoded enhancer activities. Nucleic Acids Research. 2018
- Einarsson H, et al. Promoter sequence and architecture determine expression variability and confer robustness to genetic variants. Elife. 2022
- Wenger, et al. Symmetric inheritance of parental histones governs epigenome maintenance and embryonic stem cell identity. Nature Genetics. 2023
- Sheth, Qiu, et al. Mapping enhancer-gene regulatory interactions from single-cell data. bioRxiv. 2024